Listen to this article
Study Skills
Revision tips: Mindmapping

Study Skills
Revision tips: Mindmapping

Study Skills
Revision tips: Mindmapping
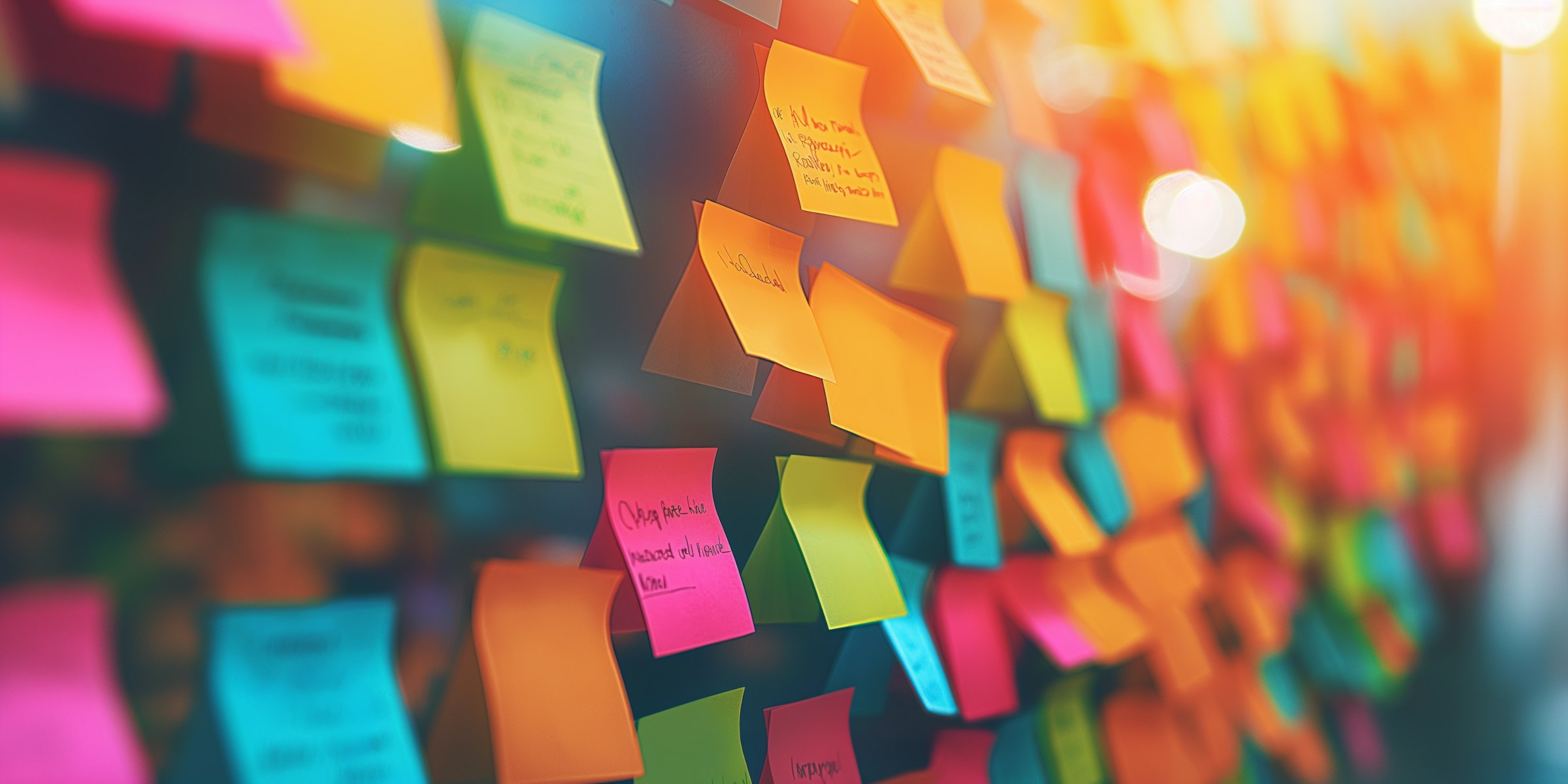


Summary
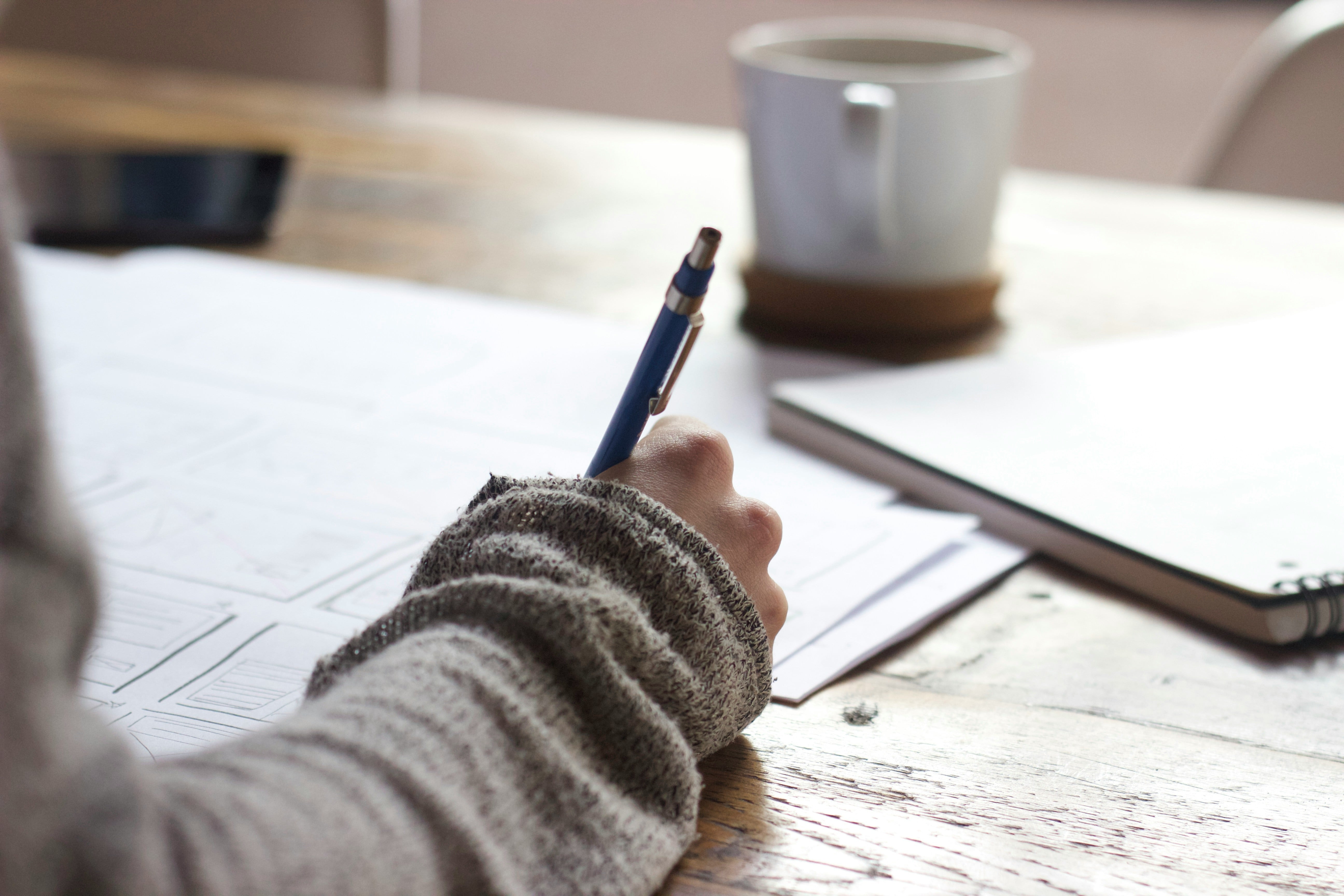
One of the key benefits of mind mapping is its emphasis on visual learning, with colours, images, and branches stimulating the brain and boosting memory retention. This multi-sensory approach engages you more effectively than traditional linear notes, allowing you to create mental associations between ideas and aiding quicker recall during exams. In the guide, we run through how to create a mindmap and how to get the most from this strategy.
Summary
One of the key benefits of mind mapping is its emphasis on visual learning, with colours, images, and branches stimulating the brain and boosting memory retention. This multi-sensory approach engages you more effectively than traditional linear notes, allowing you to create mental associations between ideas and aiding quicker recall during exams. In the guide, we run through how to create a mindmap and how to get the most from this strategy.
Read this article
4m
Creating mind maps for revision
1. Select a central topic
Begin with a central theme or topic that you need to revise. This could be a specific subject area, chapter, or concept relevant to your course material. Write this topic in the centre of your page.
2. Branch out with main ideas
From the central topic, draw branches that represent the main ideas or subtopics related to it. Use keywords or short phrases to label each branch. Keep it concise to maintain clarity.
3. Add supporting details
From each main idea branch, create additional branches to include supporting details, facts, examples, or explanations. Continue to break down concepts into smaller parts, using keywords and images where appropriate to enhance understanding.
4. Use colours and images
To make your mind map visually appealing and easier to navigate, incorporate different colours for branches and use images, icons, or symbols. This can help create associations and improve memory retention.
5. Organise and review
Once your mind map is complete, review it regularly. You can update it as you learn more about the topic or add new branches for additional details. This process can help reinforce your understanding and allow for easy review closer to exam time.
Tips for getting the most from your mind maps
1. Start with a clear goal
Before you begin creating your mind map, clarify what you want to achieve with it. Are you trying to summarise a chapter, prepare for a specific exam topic, or brainstorm ideas for an essay? Having a clear objective will guide your mapping process.
2. Software or pen and paper
Using software to create your mind maps can be much quicker and keep things more organised, but for some the process of physically writing out a mind map can be an important stage in the learning process. Work out which approach works best for you.
3. Keep it simple
Avoid overcrowding your mind map with excessive detail. Focus on key concepts and keywords rather than long sentences. This keeps the map clear and easy to review
4. Create a mind map for each topic
Rather than attempting to cover all material in one extensive mind map, create separate maps for each topic or chapter. This focused approach prevents overwhelm and makes review sessions more manageable.
5. Practice retrieval
After creating your mind map, practice recalling information by covering it and trying to recreate it from memory. This reinforces your understanding and boosts retention.
Read this article
4m
Creating mind maps for revision
1. Select a central topic
Begin with a central theme or topic that you need to revise. This could be a specific subject area, chapter, or concept relevant to your course material. Write this topic in the centre of your page.
2. Branch out with main ideas
From the central topic, draw branches that represent the main ideas or subtopics related to it. Use keywords or short phrases to label each branch. Keep it concise to maintain clarity.
3. Add supporting details
From each main idea branch, create additional branches to include supporting details, facts, examples, or explanations. Continue to break down concepts into smaller parts, using keywords and images where appropriate to enhance understanding.
4. Use colours and images
To make your mind map visually appealing and easier to navigate, incorporate different colours for branches and use images, icons, or symbols. This can help create associations and improve memory retention.
5. Organise and review
Once your mind map is complete, review it regularly. You can update it as you learn more about the topic or add new branches for additional details. This process can help reinforce your understanding and allow for easy review closer to exam time.
Tips for getting the most from your mind maps
1. Start with a clear goal
Before you begin creating your mind map, clarify what you want to achieve with it. Are you trying to summarise a chapter, prepare for a specific exam topic, or brainstorm ideas for an essay? Having a clear objective will guide your mapping process.
2. Software or pen and paper
Using software to create your mind maps can be much quicker and keep things more organised, but for some the process of physically writing out a mind map can be an important stage in the learning process. Work out which approach works best for you.
3. Keep it simple
Avoid overcrowding your mind map with excessive detail. Focus on key concepts and keywords rather than long sentences. This keeps the map clear and easy to review
4. Create a mind map for each topic
Rather than attempting to cover all material in one extensive mind map, create separate maps for each topic or chapter. This focused approach prevents overwhelm and makes review sessions more manageable.
5. Practice retrieval
After creating your mind map, practice recalling information by covering it and trying to recreate it from memory. This reinforces your understanding and boosts retention.

Written by Natalie Bull

Written by Natalie Bull
0:00/1:34
Summary
One of the key benefits of mind mapping is its emphasis on visual learning, with colours, images, and branches stimulating the brain and boosting memory retention. This multi-sensory approach engages you more effectively than traditional linear notes, allowing you to create mental associations between ideas and aiding quicker recall during exams. In the guide, we run through how to create a mindmap and how to get the most from this strategy.
Read this article
One of the key benefits of mind mapping is its emphasis on visual learning, with colours, images, and branches stimulating the brain and boosting memory retention. This multi-sensory approach engages you more effectively than traditional linear notes, allowing you to create mental associations between ideas and aiding quicker recall during exams. In the guide, we run through how to create a mindmap and how to get the most from this strategy.
Creating mind maps for revision
1. Select a central topic
Begin with a central theme or topic that you need to revise. This could be a specific subject area, chapter, or concept relevant to your course material. Write this topic in the centre of your page.
2. Branch out with main ideas
From the central topic, draw branches that represent the main ideas or subtopics related to it. Use keywords or short phrases to label each branch. Keep it concise to maintain clarity.
3. Add supporting details
From each main idea branch, create additional branches to include supporting details, facts, examples, or explanations. Continue to break down concepts into smaller parts, using keywords and images where appropriate to enhance understanding.
4. Use colours and images
To make your mind map visually appealing and easier to navigate, incorporate different colours for branches and use images, icons, or symbols. This can help create associations and improve memory retention.
5. Organise and review
Once your mind map is complete, review it regularly. You can update it as you learn more about the topic or add new branches for additional details. This process can help reinforce your understanding and allow for easy review closer to exam time.
Tips for getting the most from your mind maps
1. Start with a clear goal
Before you begin creating your mind map, clarify what you want to achieve with it. Are you trying to summarise a chapter, prepare for a specific exam topic, or brainstorm ideas for an essay? Having a clear objective will guide your mapping process.
2. Software or pen and paper
Using software to create your mind maps can be much quicker and keep things more organised, but for some the process of physically writing out a mind map can be an important stage in the learning process. Work out which approach works best for you.
3. Keep it simple
Avoid overcrowding your mind map with excessive detail. Focus on key concepts and keywords rather than long sentences. This keeps the map clear and easy to review
4. Create a mind map for each topic
Rather than attempting to cover all material in one extensive mind map, create separate maps for each topic or chapter. This focused approach prevents overwhelm and makes review sessions more manageable.
5. Practice retrieval
After creating your mind map, practice recalling information by covering it and trying to recreate it from memory. This reinforces your understanding and boosts retention.

Written by Natalie Bull
Nat is Booost Education’s copywriter and artist-in-residence and brings considerable authenticity to our marketing content through her own expertise and experience from supporting DSA students and her neurodivergent son.

Written by Natalie Bull
Nat is Booost Education’s copywriter and artist-in-residence and brings considerable authenticity to our marketing content through her own expertise and experience from supporting DSA students and her neurodivergent son.



